How to Do Thematic Analysis in Qualitative Research
There's a moment in every qualitative research project when you step back and look at your pile of transcripts and wonder, "What's the story here?" Thematic analysis (TA) helps you discover key patterns that tell that narrative.
Whether exploring patient experiences in healthcare, investigating organizational culture, or studying social movements, thematic analysis gives you a flexible yet thorough way to understand people's experiences. But if you’re new to TA, it’s normal to worry about not doing it "right" or missing key details.
This article walks you through thematic analysis, from practical steps for coding to your final narrative. You'll also learn to confidently analyze your data using computer-assisted qualitative data analysis (CAQDAS) tools like Delve to manage your tedious tasks - like organizing transcripts, tracking codes, and maintaining your codebook.
Unlocking the story of your data
Turning hundreds of codes into meaningful themes is hard, but Delve's intuitive interface simplifies the process. Tools like code nesting and collaborative features help organize your analysis while keeping your focus on finding important patterns.
Overview: Braun & Clarke's six steps of thematic analysis
Thematic analysis helps you make sense of unstructured qualitative data by transforming data like raw interviews and field notes into a coherent narrative about your research questions. Instead of just listing what people said or did, you look for meaningful patterns that tell you how they really experienced something.
There's no single 'right way' to do thematic analysis, which can feel overwhelming. You move back and forth between your data and your insights, and your theoretical background, research questions, and experiences ultimately shape what you see along the way. Reflexivity helps you harness these interpretations, rather than aiming for objectivity.
For the past two decades, students and new researchers have found solid ground in Braun and Clarke's six steps the pair offered in their 2006 paper, Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology.
As we’ll explore, their highly cited six-step approach shows how to be systematic yet flexible with your data:
Familiarizing yourself with the data - Begin by immersing yourself in your transcripts through repeated reading and note-taking to identify initial ideas and patterns.
Generating initial codes - Start identifying and labeling your data with codes that capture the key concepts, patterns, or features you observe.
Collating codes with supporting data - Group related excerpts by code, ensuring each one is linked to a specific idea or pattern you want to explore further.
Grouping codes into themes - Organize the codes into broader themes, finding patterns that connect related concepts and highlight key insights in your data.
Reviewing and refining themes - Refine and revise your themes by ensuring they’re distinct, well-supported, and relevant to the research question, merging or eliminating themes as needed.
Producing your report - Write your report that tells a coherent story that ties back to your research questions while highlighting the broader significance of your findings.
These steps will guide your thematic analysis, and we'll dig into each one as we go.
🌐 Real world thematic analysis
Consider a recent study on how students adapted to online learning during COVID-19 by Yeung & Yau (2022). Through thematic analysis, they uncovered fascinating patterns in students' experiences, from study environment challenges to emotional responses to online classes. Their analysis revealed not just problems, but how students developed new learning strategies and what support they needed most.
What is a theme in qualitative research?
Qualitative codes are building blocks for your themes. They label meaningful snippets in your data - from recurring patterns to interesting insights. As you fill your codebook with these pieces of meaning, and as you define and analyze them, you'll discover how they connect and overlap. These connections become your themes.
Think of codes as puzzle pieces that give your thematic analysis meaning. Each one captures a slice of meaning from your data that hints at a pattern. These connections become your themes. These patterns can be shared experiences, common reactions, or repeated ways of understanding a situation.
Your themes will tell the broader story about what it all means as a whole. This broader understanding comes from looking beyond the immediate details and thinking about the larger context you might otherwise miss.
🏗️ Coding as Your Foundation: Master the fundamentals with our free qualitative coding course or explore our comprehensive guide. For hands-on experience, try Delve's free trial to start coding your qualitative data more efficiently and effectively today.
Themes help you answer, “So what?”
As Braun and Clarke explain, a theme “captures something important about the data in relation to the research question and represents some level of patterned response or meaning.” They suggest focusing on interpretation rather than simple categorization when developing themes. In their eyes, a “good” theme:
Tells a clear story about a pattern in your data
Connects directly to your research questions
Goes beyond describing to offer deeper insights
Is backed by evidence across your dataset
Distinguishes itself from other themes but fits the broader analysis
Themes help you answer "So what?" by revealing deeper meaning in your data. In Yeung & Yau’s online learning study, themes like "Self-Regulated Learning Strategies" went beyond describing technical problems to show how students adapted to virtual learning, illuminating broader implications for education.
But how do you transform these individual codes into meaningful themes, and tell a richer story about what’s really going on? Your unique interpretation plays a key role.
🔍 Deriving themes: From description to deeper insights
Say you want to study how telehealth is impacting healthcare workers instead of remote learning for students. A weak theme, such as "Technology Use in Virtual Care," merely describes what participants did. A strong theme—like "Digital Transformation of Medical Intimacy," interprets how technology alters healthcare relationships. To develop themes, consider the story a pattern tells, its significance, its relevance to your research questions, and the deeper insight it reveals.
Reflexivity in thematic analysis
Themes don't magically rise out from your data on their own. You derive them through your interpretation and analysis. As Braun and Clarke emphasize, you're not just a passive observer in this process.
To say themes “emerge” from your data downplays your active role in identifying patterns and deciding what matters. Your expertise, background, and research questions all shape what patterns you notice and which ones matter most. Every time you create a code or group similar ideas, you're actively interpreting your data.
This is why reflexivity is critical. By consistently writing memos about your thought process and acknowledging how your perspective influences what you see, you strengthen your analysis and makes it more transparent. Your open engagement with the data not only develops richer themes but instills more trust in your findings.
Engaging with your data for richer analysis
If you're analyzing interviews about healthcare workers transitioning to virtual care, your own experience as a healthcare provider might help you notice important nuances in your data. When a nurse mentions feeling disconnected from patients, you might recognize this isn't just about technical challenges. You think it might be more about fundamental changes in how care relationships work. A colleague with a different background might and probably will notice entirely different things.
Whether you’re a nurse studying telehealth, a former educator examining the impact of virtual learning, or a student doing their first thematic analysis, your work benefits from documenting your unique insights with reflexive memos With Delve, you can quickly code excerpts and attach memos that never got lost in the shuffle or misassigned:
Whether you're building understanding from your participants' stories (inductive thematic analysis) or testing existing theories (deductive thematic analysis), your perspective guides how you interpret the data. The key is being transparent about how your background shapes your analysis. This doesn't make your findings less valid - it makes them more honest and gives your readers important context about your results.
🔍 Reflection vs. Reflexivity in Thematic Analysis:
While approaches like Joffe's 2012 content-driven method stick closely to predefined steps, Braun and Clarke advocate for a more dynamic role in analysis, emphasizing that researchers actively shape their findings.
- Reflection: Similar to glancing in a mirror, you observe and note what the data shows, taking it at face value.
- Reflexivity: Going a step further, you examine how your own views and experiences influence what you see and the conclusions you draw, making your analysis richer and more nuanced.

Curious to learn more? Deepen your understanding of reflexivity with Understanding Reflexive Thematic Analysis.
When to use thematic analysis
Thematic analysis shines when studying complex experiences through interviews, focus groups, or field observations. It's particularly valuable when you want to understand how people respond to situations, like healthcare workers adapting to telehealth or students navigating online learning.
By uncovering patterns in changing behaviors, emotional responses, and evolving relationships, thematic analysis reveals insights that more structured approaches, like qualitative content analysis, might miss.
Choose thematic analysis when you want to understand the "how" and "why" behind experiences, not just the "what." It's especially useful for:
Understanding complex experiences in depth
Exploring how people respond to situations
Finding patterns across different perspectives
Studying under-researched areas
Answering questions about meaning rather than measurement
Maintaining flexibility in your analysis
While you'll sometimes see thematic analysis and content analysis used interchangeably, they serve different purposes. Content analysis works well for gauging patterns across large amounts of text data, like analyzing news articles or social media posts. Thematic analysis, as we saw in Yeung & Yau's study of online learning, helps you understand deeper meanings from data like interviews - not just what challenges students faced but how they made sense of these experiences and adapted.
Before jumping into your work, take time to consider what data will best help answer your research questions. Whether you're working with interviews, observations, or other materials, you'll want clear processes for organizing and interpreting your data. CAQDAS like Delve keeps all your transcripts, codes, and notes in one place, making it easier to spot meaningful patterns as they develop.
Now that we understand when and why to use thematic analysis, let's look at how to do it.
🧭 Think like a research instrument
Remember, your expertise and viewpoint are essential tools for analyzing your data. By staying conscious of how your perspective influences your interpretation through reflexivity, you can offer clearer, more transparent insights into the patterns you uncover in your research.
Learn more about reflexivity Understanding Reflexive Thematic Analysis.
Step-by-step thematic analysis guide
Whether analyzing interviews about telehealth adoption, understanding essential workers' pandemic experiences, or any other topic—Braun and Clarke’s six-step framework provides structure while remaining flexible enough for deep analysis.
Let’s walk through each the thematic analysis steps as if exploring our virtual healthcare example from earlier, transforming these raw interviews into meaningful insights about healthcare delivery in a remote-first landscape.
1. Familiarizing yourself with the data
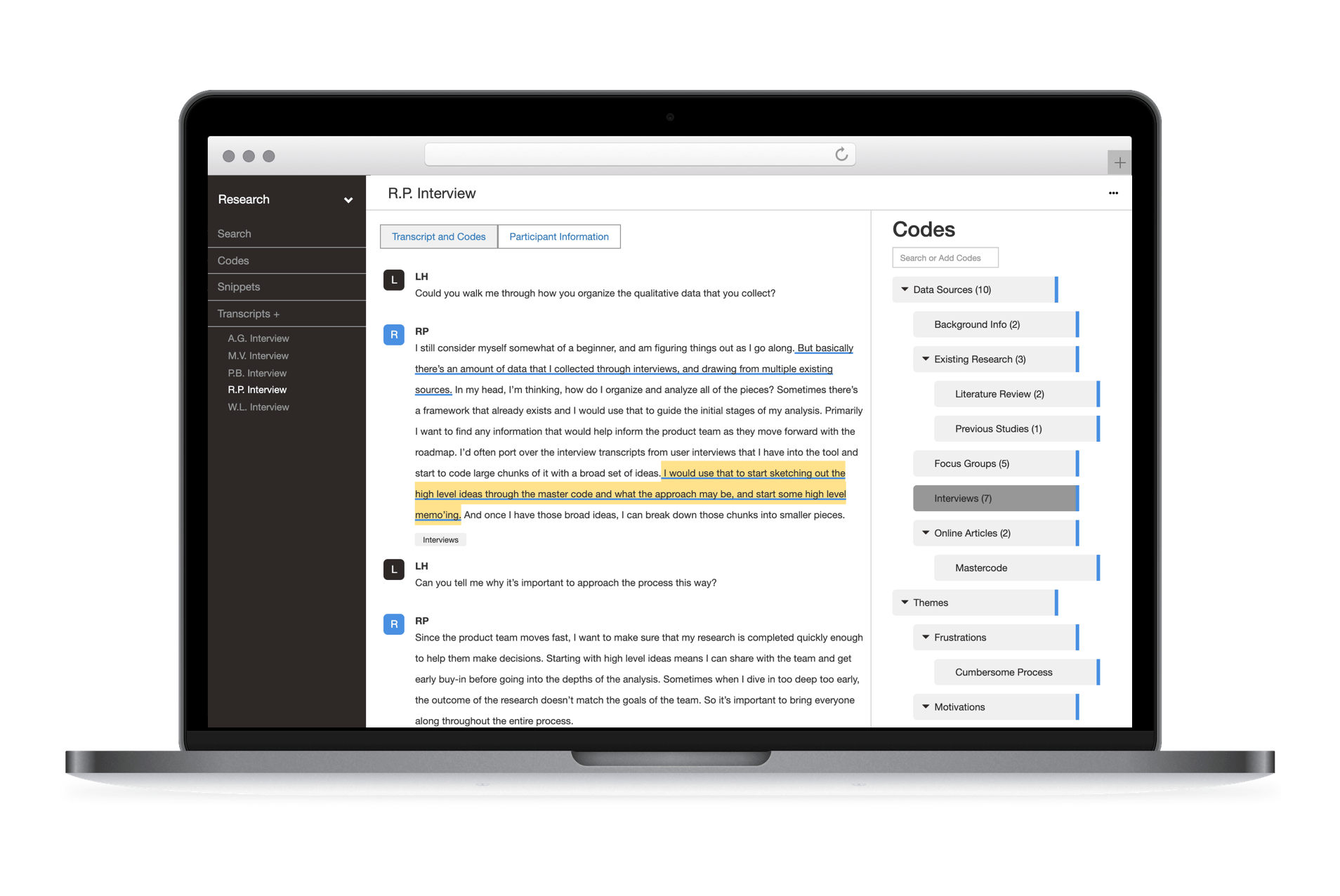
Start by diving into your materials and getting to know them inside out. Read through everything at least twice—once to get a general sense of the data, and again to spot recurring ideas and patterns that stand out. This isn’t the time to code yet—it’s about understanding the big picture and jotting down notes that may guide you later.
In our telehealth example, that means reviewing each transcript with an eye on how doctors, nurses, and administrators experience virtual care. You pay special attention to any mention of challenges or shifts in patient-provider interactions to understand how virtual care is reshaping these encounters.
Best practices:
Take detailed notes during your first reading
Mark interesting passages without formally coding yet
Write initial memos about potential patterns
Note questions or gaps that need deeper exploration
Record your early impressions and assumptions
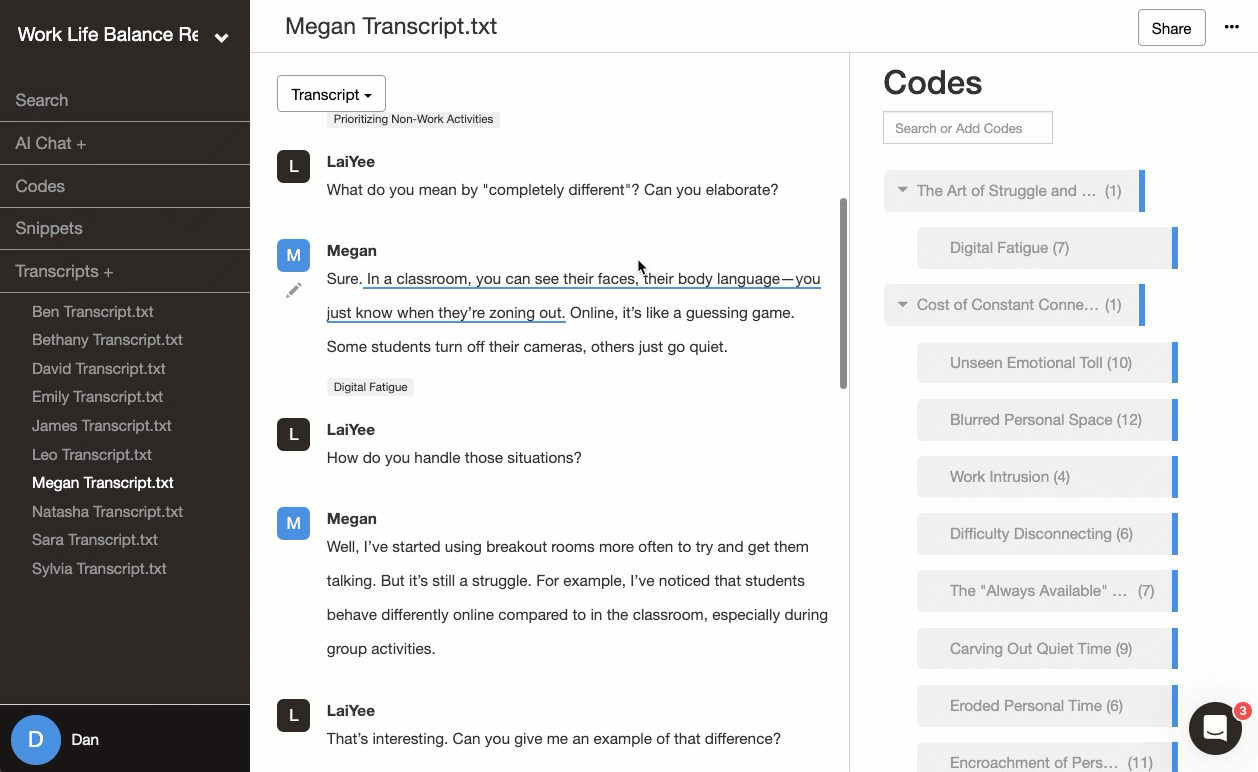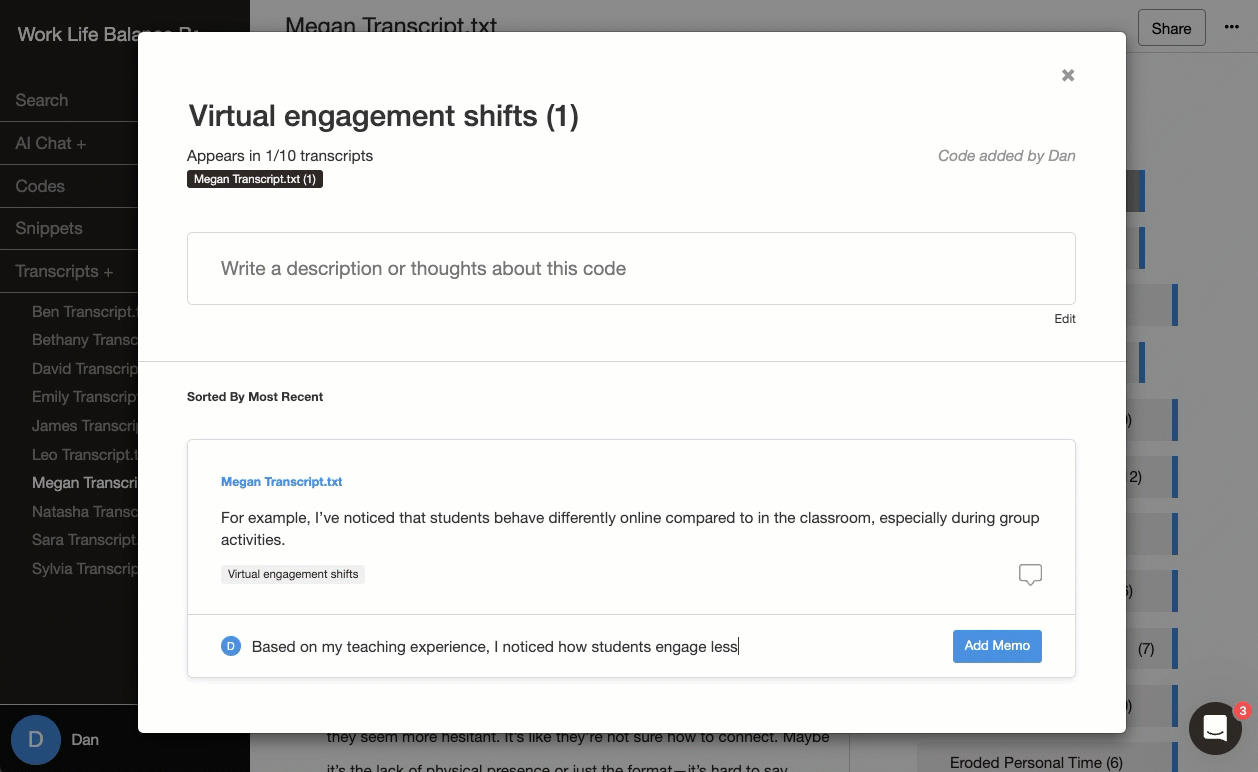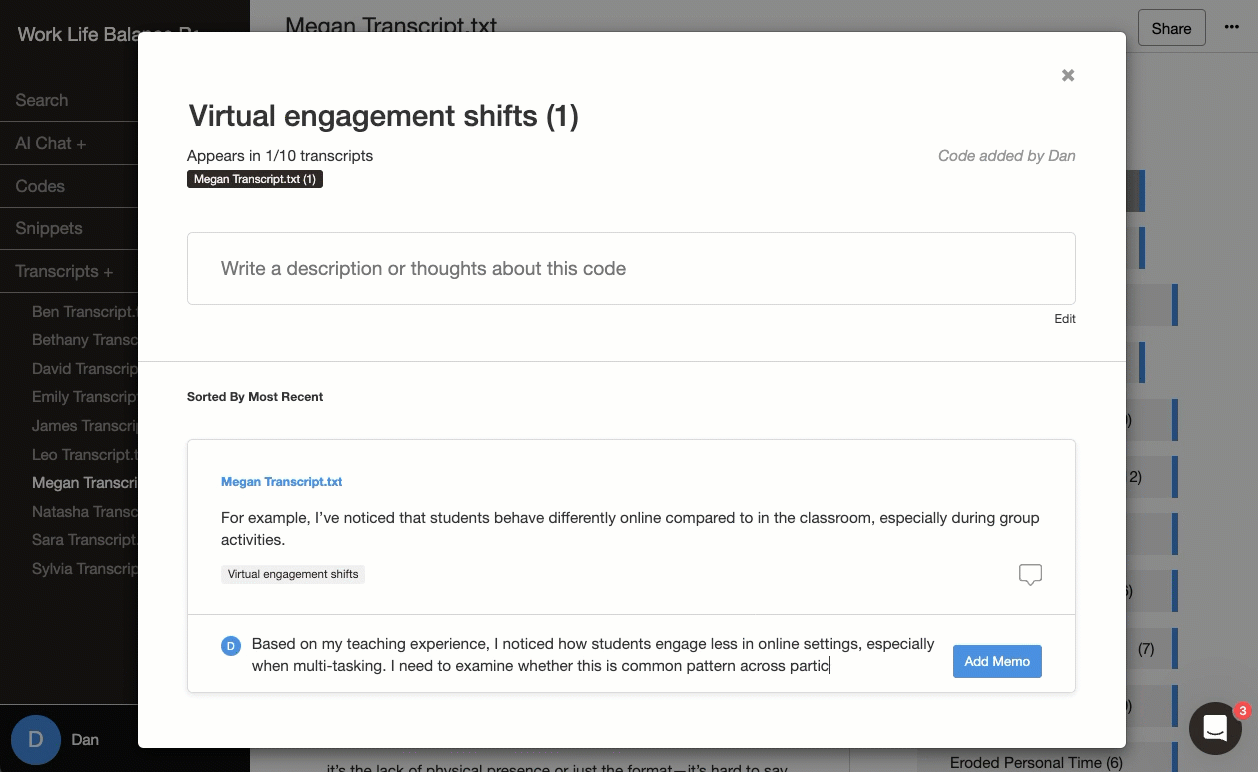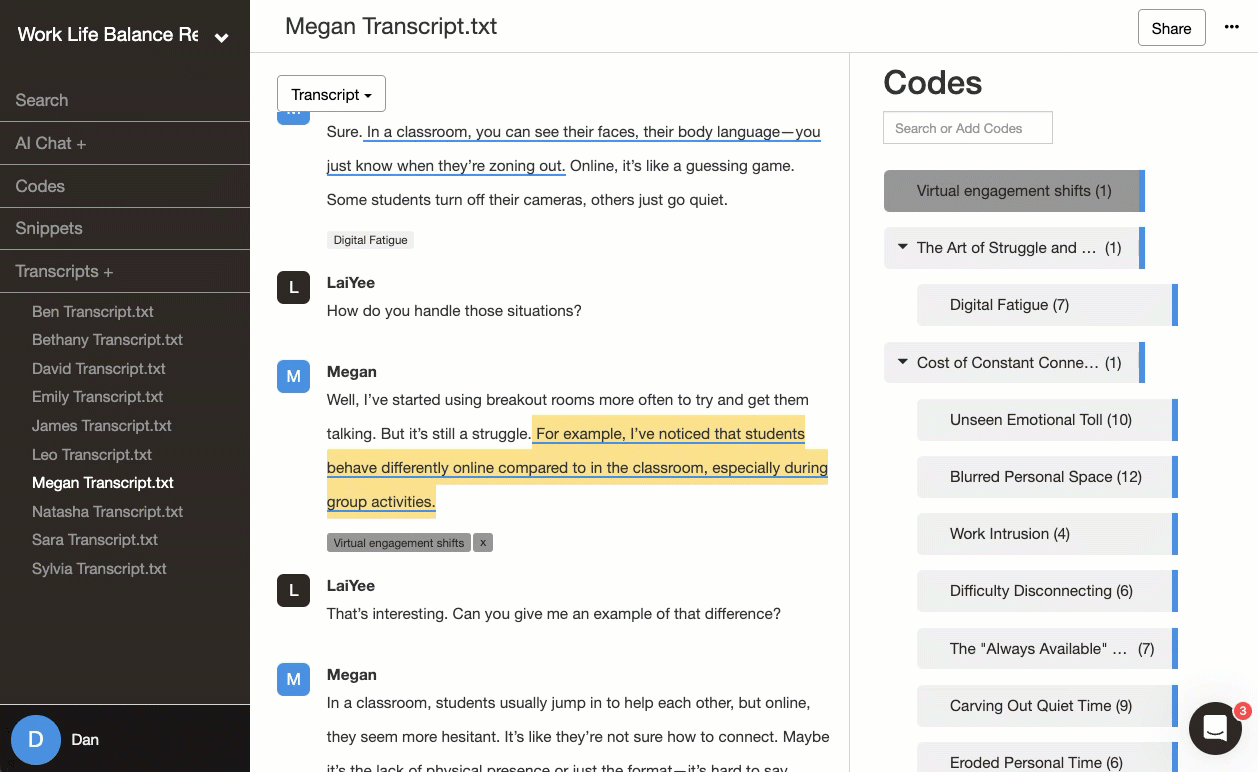
📝 Making memos matter
The journey from raw data to meaningful themes isn't linear - it's a process of active discovery and refinement. Your analytical memos serve as a compass, capturing your developing insights and decisions. When you're immersed in analysis, tracing how specific codes led to broader themes, your memos map out your thinking process.
- Creates a valuable record of your analytical decisions
- Deepens awareness of how your perspective shapes interpretations
- Makes your research process transparent and credible
- Here's how easy it is with Delve
2. Generating initial codes
Once you’re comfortable with the data, begin your initial coding. These codes act as the building blocks for your themes later. Focus on identifying meaningful patterns or recurring ideas, but don’t worry about getting everything perfect on the first pass—this is just the beginning. Codes should be descriptive but flexible enough to allow for refinement later.
In our telehealth scenario, you might start with codes like “screen fatigue,” “loss of casual connections,” “missing physical presence,” or “technical frustrations.” These capture recurring experiences shared across multiple transcripts and highlight areas worth exploring further.
📄 Telehealth Adaptation - Reflecting on Digital Shifts
"Initially, I thought virtual consultations would be an adjustment for a week or two. But as weeks turned into months, the lack of physical presence1 and the increased screen time2 began to wear me down. I miss the informal chats with patients3 that happened as they walked out the door. Now, everything feels more transactional4, like we're just ticking boxes."
Codes:
- 1 Missing physical presence
- 2 Screen fatigue
- 3 Loss of casual connections
- 4 Formalized patient interactions
Best practices:
Start with broad, inclusive codes
Use participants’ own words (in vivo coding) when possible
Maintain a codebook with definition
Document any changes or additions to your codes over time
Use Delve to easily keep track of data excerpts and memos
📌 Tips for developing richer themes
When coding your interviews, you might notice recurring mentions of "lost informal moments." This initial code might lead you to explore how the shift to telehealth affected casual interactions that traditionally happened before or after appointments. These unstructured exchanges often carry crucial emotional or social weight. Delve lets you attach memos to these codes, helping you develop deeper changes in patient and staff relationships as you go. These insights seed your themes for later!
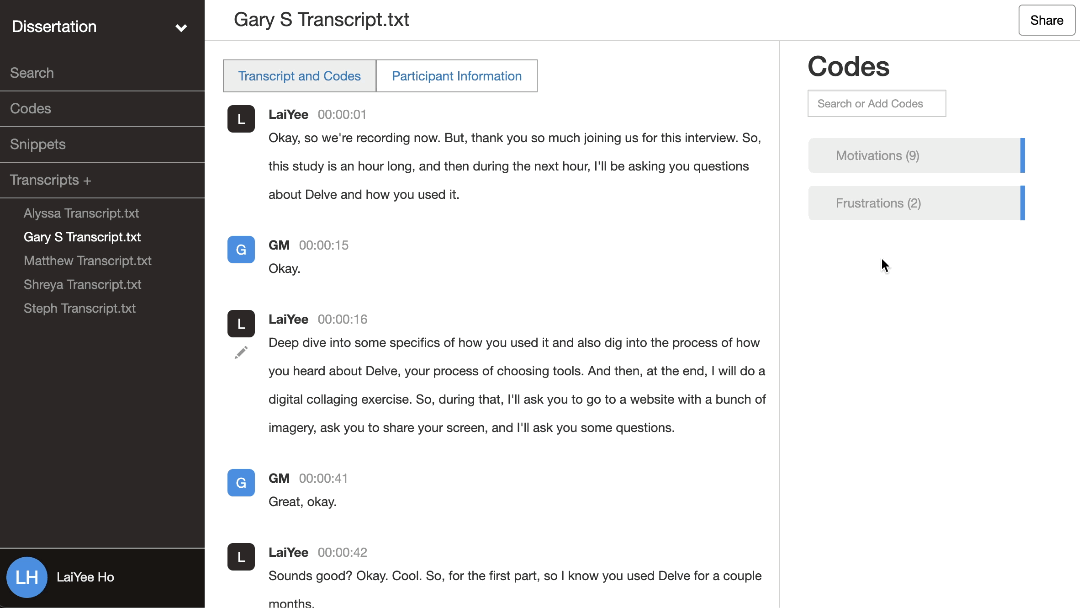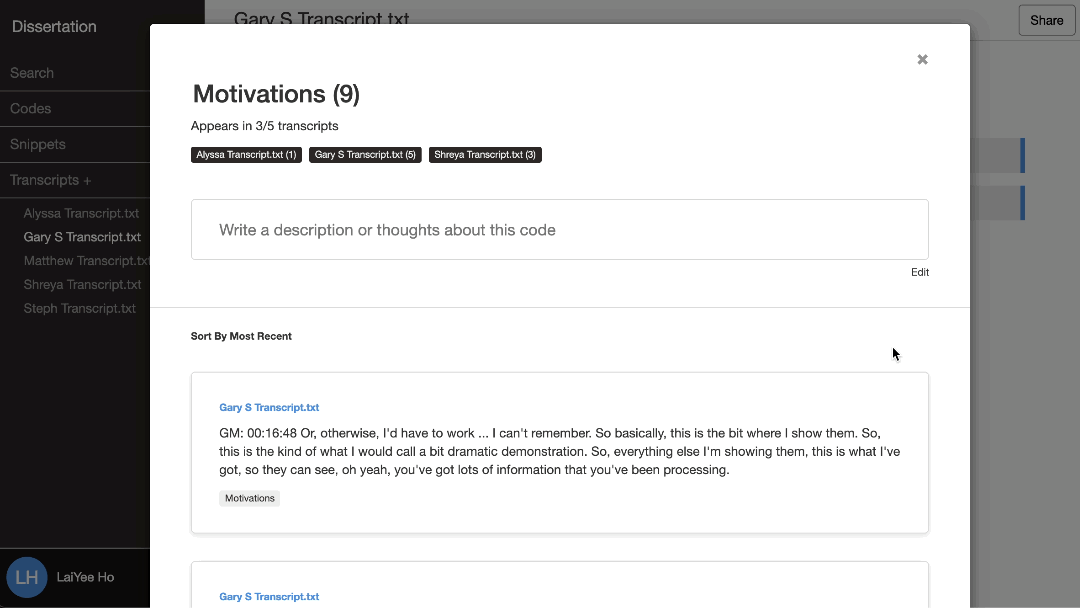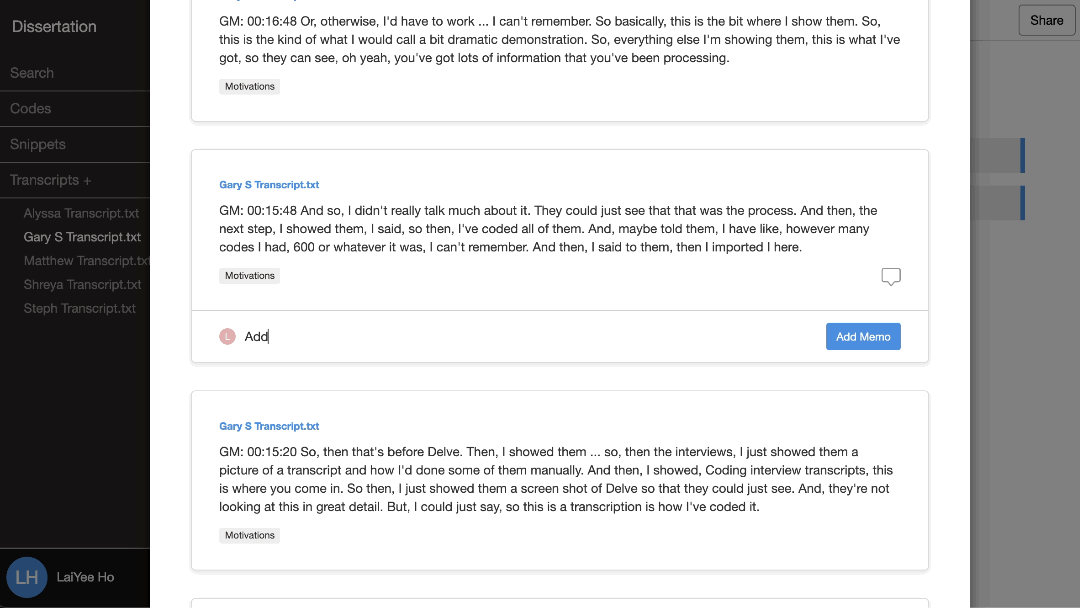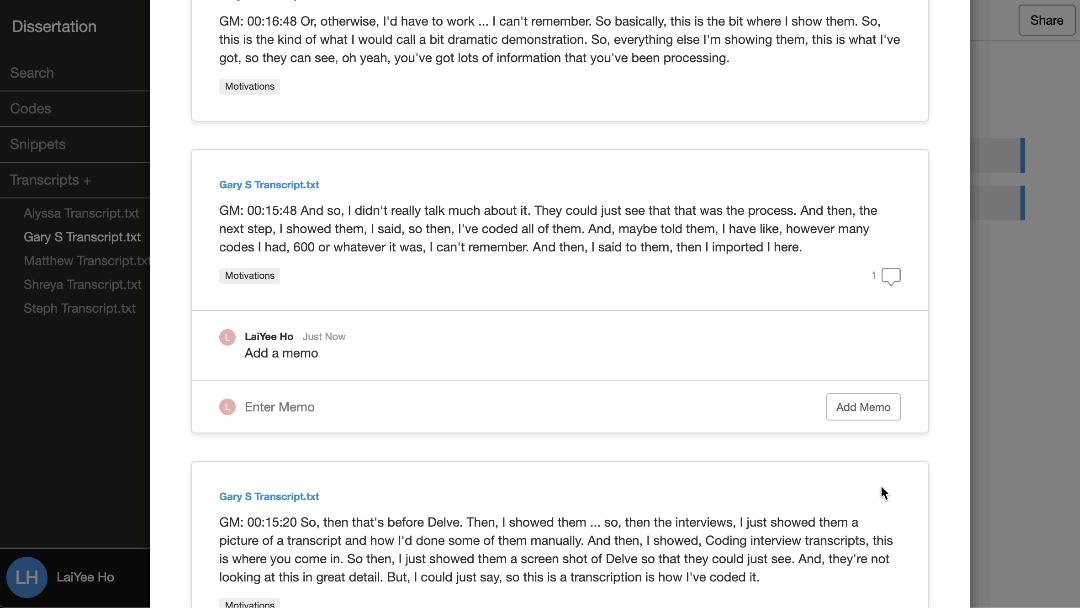
3. Collating codes with supporting data
Once you’ve created your codes, cluster together all excerpts that share the same code. This is where you organize rough ideas from your raw data and start identifying possible connections between them. With Delve, you can nest related codes together, move ideas around, and reorganize them flexibly as you discover new connections.
For our telehealth example, gather all quotes labeled “loss of casual connections.” Then, do the same for the other codes. Along with the nesting feature, reviewing all snippets under each code in Delve’s code page view can reveal unexpected connections and help you see how different codes intersect. As you read through each one, you might start noticing how these challenges impact patient-provider relationships in similar ways, sparking ideas for broader themes. Use your memos to track your thinking and explore their broader implications.
🗺️ Mapping connections: Visual tools can help you see relationships between codes. Whether using software features like co-occurrence matrices or creating manual maps, visualizing these connections often reveals patterns you might have missed.
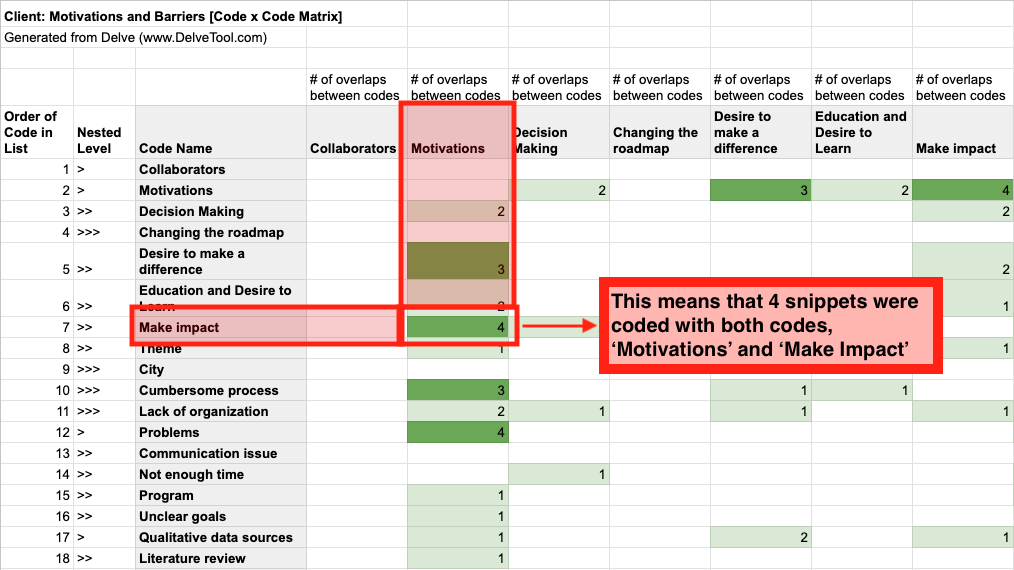
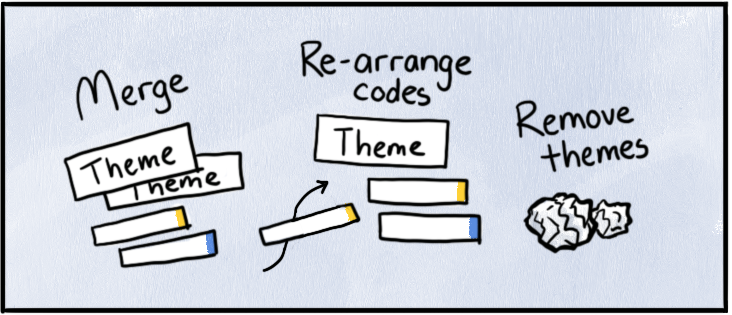
4. Grouping codes, searching for themes
Now it's time to step back and ask: What bigger story are these codes telling? Group related codes into broader themes that reflect key patterns in your data. This step transitions your focus from isolated ideas to bigger, overarching insights, shifting from descriptive coding to more interpretive analysis. It’s worth repeating that memos makes it easier to know where you stand as you work and explain these decisions in your write-up.
In our telehealth example: Codes like "missing physical presence," "loss of casual connections," "screen fatigue," and "digital waiting rooms" might combine into a theme like "Transformed Medical Encounters." You're not sure yet, but you think you've captured something new about virtual care interactions—more than just how they deal with new technology or remote work.
Potential Theme: ?
We are analyzing how the following codes might converge to outline emerging themes within the telehealth experience.
Code: Missing Physical Presence
Definition: Examines the impact of the absence of face-to-face interaction, emphasizing its significance in patient comfort and relationship building.
Code: Screen Fatigue
Definition: Captures the weariness and discomfort stemming from excessive use of digital screens, affecting both patients and providers.
Code: Digital Waiting Rooms
Definition: Focuses on the changes in the waiting experience, highlighting shifts in patient engagement and clinic workflow.
Key theme review steps:
Read all data excerpts for each theme
Check if themes are distinct enough
Look for sub-themes within larger themes
Consider if themes need splitting or combining
Verify each theme has sufficient supporting data
🤝 Strengthening Your Analysis: Consider having peers review your themes. Fresh perspectives from peer reviewing often help identify assumptions or gaps in your analysis. Tools like Delve make it easier to share your work and gather feedback—or work and code collaboratively as a team.
5. Reviewing and refining your themes
You’re honing in on the main idea behind each theme and deciding how all your findings fit together into a coherent story. Take a closer look at your themes to ensure they’re clear, distinct, and backed by enough data. Merge themes that overlap, and split any that feel too broad. You should clearly articulate why each one matters and how they help answer your overarching research questions.
In our telehealth example: “Technology challenges” might initially seem like one theme, but on review, it could split into two sub-themes: “user frustrations” and “technical learning curves.” Meanwhile, “Transformed Medical Encounters” might evolve to include sub-themes like “emotional disconnection” and “formalized interactions.”
Theme: Transformed Medical Encounters
This theme elaborates on how digital transformations have reshaped the dynamics of patient-provider interactions, underlining significant shifts in communication and care delivery.
Sub-theme: Emotional Disconnection
Code: Missing Physical Presence
Examines the impact of the absence of face-to-face interaction, emphasizing its significance in patient comfort and relationship building.
Code: Screen Fatigue
Captures the weariness and discomfort stemming from excessive use of digital screens, affecting both patients and providers.
Sub-theme: Formalized Interactions
Code: Digital Waiting Rooms
Focuses on the changes in the waiting experience, highlighting shifts in patient engagement and clinic workflow.
Code: Technology Challenges
Describes the difficulties encountered by patients and staff as they navigate new digital tools and platforms.
Reference: Delve Qualitative Data Analysis Software
Best practices:
Revisit your data to confirm that each theme has strong supporting evidence.
Refine themes to ensure they’re distinct and meaningful.
Start organizing your themes into a coherent structure for your report.
📖 Building a Narrative: Start weaving your identified themes into a narrative structure that tells a compelling story of your findings. This involves arranging themes in a logical sequence that enhances the reader's understanding and drives home the key insights of your research.
6. Writing your report
This is where everything comes together. Write a narrative that connects your themes back to your research questions, illustrating each with vivid quotes and clear insights. These direct quotes or anecdotes from your data bring each theme to life and connect them directly to the questions driving your research.
In our telehealth example: A theme like “Transformed Medical Encounters” could include participant quotes like, “It’s harder to read patient emotions over a screen,” to highlight the emotional and practical changes in virtual care. Your report should weave these insights into a compelling story that answers your research questions.
Key Insights: Navigating Telehealth's New Norms
Our thematic analysis revealed significant shifts in patient-provider interactions within telehealth, highlighting both challenges and opportunities.
- Key Quote: "It’s harder to read patient emotions over a screen" – emphasizes the need for new communication strategies.
- Recommendation: Enhance provider training on digital engagement techniques to reduce emotional disconnect.
Incorporating technology thoughtfully is crucial to maintain the personal touch in patient care. Future strategies should focus on technological empathy to ensure a balanced healthcare experience.
Reference: Delve Qualitative Data Analysis Software
Here, you might write that these themes capture how telehealth fundamentally alters patient-provider relationships. From the emotional ripple effects of being physically apart to the practical adjustments in online waiting rooms and at-home clinical spaces, it’s all connected.
Report writing tips:
Structure your report clearly around each theme.
Use participant quotes to bring themes to life.
Show relationships between themes, e.g. data visualization.
Address alternative interpretations to add depth to your findings.
Connect to existing literature, where possible.
Acknowledge any limitations.

A top-rated tool for thematic analysis
“Delve supported me through thematic analysis without automating too much. I could explore patterns across transcripts without losing control of the process.” — Bev C., Researcher
Try Delve Free for 14 DaysNo commitment. Cancel anytime.
Common challenges (and top solutions) for thematic analysis
Thematic analysis can help you make sense of your data, but it’s not always smooth sailing. You're not alone if you’ve felt overwhelmed by endless codes, struggled to form themes, or faced hiccups working with a team. Let’s walk through some of the biggest challenges—and how Delve’s top-rated tool helps you handle them.
Challenge 1: Overwhelming amounts of data and codes
What happens: You start coding, and before you know it, you’re swimming in hundreds (or thousands) of codes. Similar ideas get labeled differently, making it hard to see patterns. It can feel like trying to piece together a puzzle while constantly losing the edges. Delve simplifies this chaos by creating a centralized workspace where you easily upload everything—from transcripts to memos—to keep them at your fingertips.
How Delve helps
Centralized Coding: Keep all your transcripts, codes, and memos in a centralized workplace so nothing gets lost. Learn how Delve easily organizes your project here.
Code Organization: Merge duplicate codes or group similar ones with simple drag-and-drop tools. See how easy-to-use nesting tools simplify your analysis.
Smart Search Tools: Quickly locate codes, excerpts, and memos across your entire project with universal search. Read how Delve saves time and ensures nothing slips through the cracks.
Challenge 2: Moving from codes to themes
What happens: Most teams struggle with organizing codes and seeing how they connect to form meaningful themes. Basic tools like Excel or Airtable only allow flat, single-level coding – imagine trying to organize a complex analysis with just hashtags. The more data you add to this system, the more overwhelming it becomes to manage.
Delve takes a different approach with nested hierarchies of codes. Create parent themes with related child codes underneath, helping you move from descriptive labels to deeper analysis. For example, in our remote learning study, you might have "Technical Barriers" with nested codes for "Internet Issues," "Software Problems," and "Device Access."
How Delve helps
Visual Mapping: Tools like code co-occurrence matrices show you where codes overlap, giving you a clear starting point for identifying themes. Explore how to spot patterns with co-occurrence matrices.
Memo Linking: Attach memos directly to your codes to track your thought process as themes begin to take shape. Learn how to use Delve memos effectively.
Challenge 3: Maintaining analytical rigor
What happens: Summarizing what participants said is one thing but explaining why it matters is another. The leap from raw data to deeper insights can feel daunting. Without a clear transition point, your analysis risks falling flat. Keeping track of all the details while maintaining a cohesive narrative is challenging enough, let alone juggling sticky notes, spreadsheets, and scattered files. This is where practicing reflexivity is key.
How Delve helps
Analytical Memos: These memos capture your reasoning as you interpret data. They help bridge the gap between “what” and “why” and track your thought process during analysis.
Reflexive Memos: Reflexive memos also make it easier to stay aware of your biases and assumptions to keep your analysis transparent and grounded.
Universal Search: Quickly find excerpts to revisit critical points without disrupting your workflow.
Connected Memos: Unlike paper notes that can get separated from your data, Delve memos stay linked directly to their relevant transcript sections
Challenge 4: Coordinating a team effort
What happens: Working with a team sounds great—until different people label data inconsistently or you lose track of versions. Remote work adds another wrinkle, making it hard to stay aligned and efficient. Collaboration can quickly turn into confusion without the right tools.
How Delve helps
Collaborative Coding: Work together in real time, seeing everyone’s contributions in a shared project. Learn how to collaborate in Delve.
Standardized Codebooks: Set clear definitions for codes to ensure everyone’s on the same page. See how to add code definitions with Delve.
Streamlined Sharing: Share your analysis with teammates or advisors for peer review without endless file juggling. It’s easy and safe to share your work with Delve.
Live Codebook Updates: Your web-based codebook updates live for everyone on your team. This is much more efficient than passing a Word doc or Excel sheet back and forth.
Tools for thematic analysis
Thematic analysis involves identifying patterns, creating codes, and arranging them into themes. As you work, you'll iterate on these themes by merging, re-arranging, and re-naming codes. The problem with traditional tools like sticky notes, spreadsheets, and word processors is they quickly become chaotic with larger datasets. Other qualitative analysis software exists, but most come with steep learning curves, high price tags, or both.
Delve is the best tool for thematic analysis.
Don't just take our word for it. From first time researchers to professors, check out what customers say about Delve:
“We were able to easily collaborate and facilitate our thematic analysis process without a steep learning curve and at a very reasonable price.” Nate S.
“Delve helped me to organize and code qualitative research for my doctoral dissertation. It was very easy to use and intuitive in its use. The tools I used took me from organizing my transcripts to first and second-round coding through thematic analysis.” Lisa G.
“I wanted to complete the thematic analysis of my research results and the Delve software made the process very smooth for me.” -Kopi S.
▶ Watch more from real users, then try it for free
Hear why Tommy, a university professor, recommends Delve to anyone doing thematic analysis.
No commitment. Cancel anytime.
Learn more about thematic analysis
These resources explore specific approaches, tools, and techniques for thematic analysis:
Inductive vs. Deductive Thematic Analysis – Compare building themes from data and testing existing theories
Reflexive Thematic Analysis – Learn how your perspective shapes analysis and why that matters
Building a Codebook for Thematic Analysis – Create clear, consistent code definitions for your research
Grounded Theory vs. Thematic Analysis – Compare two popular qualitative approaches
Coding Reliability in Thematic Analysis – Ensure consistency when coding with a team
Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis vs. Thematic Analysis – When to use each approach
Collaborative Thematic Analysis – Best practices for team-based qualitative research
Learn about other ways to analyze qualitative research.
Thematic analysis is just one approach of many ways to analyze qualitative research. To read more about other types of coding, read our Essential Guide to Coding Qualitative Data.
References
Virginia Braun & Victoria Clarke (2006) Using thematic analysis in psychology, Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3:2, 77-101, DOI: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Joffe, H. (2011). Thematic Analysis. In Qualitative Research Methods in Mental Health and Psychotherapy (eds D. Harper and A.R. Thompson). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119973249.ch15
Cite this blog post:
Delve, Ho, L., & Limpaecher, A. (2020a, August 31). How to Do Thematic Analysis. Essential Guide to Coding Qualitative Data. https://delvetool.com/blog/thematicanalysis