AI Features in QDA Software: What Actually Works (And What Doesn't)
AI features are now part of many qualitative coding software platforms. It’s a genuine watershed moment for qualitative research with automatic pattern recognition, instant summaries, and coding suggestions that catch what you might miss. These capabilities are already transforming how we work.
But not all AI tools for qualitative data analysis approach things the same way. Some have no AI capabilities whatsoever. Some tools deliver genuine breakthroughs that speed up analysis without sacrificing nuance. Others provide little more than glorified keyword searches disguised as artificial intelligence.
This uneven AI landscape also raises some important questions:
Will my own thoughts still be at the center of my analysis?
Will this save me time, slow me down, or hurt the quality of my work?
How transparent is the AI decision-making process?
We sat down with the top AI-assisted QDA platforms to answer these questions. Our takeaway is that the best AI for qualitative data analysis took on the tedious tasks, helped spot initial patterns, and saved us a good chunk of time (in some cases). But the interpretation and meaning-making? That still takes a human touch.
🤖 Beyond the AI hype: What really matters to researchers
Qualitative analysis and AI both rely on pattern recognition, looking for recurring words, concepts, and ideas to create context and make sense of larger meanings. But human researchers bring lived experience, cultural nuance, and the ability to read between the lines to understand the why behind those patterns. These are interpretive skills that AI can mimic but not truly replicate.
So let's be clear about what we really look for from AI support:
Enhancement, not replacement. AI can handle mechanical tasks like applying established codes, organizing data, and spotting initial patterns. Interpretation is up to you. Tools that promise to "do the analysis" typically miss the nuanced thinking that makes qualitative research valuable.
Transparency over black boxes. Good AI tools explain their reasoning and show you exactly why they suggested specific codes or patterns. If the AI can't tell you how it reached a conclusion, or show you the source for their thinking, you can't validate whether it makes sense for your data.
Methodological awareness. The best AI features understand they're supporting qualitative methodology, not trying to turn your research into quantitative analysis. They complement your analytical process by taking over some of the grunt work rather than trying to automate it away.
With what matters in mind, let's look at how the major AI-supported QDA platforms stack up.
“The best AI for qualitative data analysis knows that qualitative methodology isn’t quantitative analysis in disguise. It does the grunt work so you can do more of the deep thinking work.”
NVivo: Enterprise AI with comprehensive features
We spent the better part of a week just getting NVivo set up for our team. The first day was figuring out which version to use, then a few days of trial and error on how the AI Assistant actually works with our coding workflow. But when it finally clicked, the AI genuinely impressed us with what it could handle.
The AI processes multiple file types – audio, video, PDFs, and text – in different languages. It can automatically summarize documents and apply three auto-coding approaches: pattern-based coding that learns from your existing work, thematic auto-coding using language packs, and AI-suggested child codes with evidence-based recommendations. You also get sentiment analysis that creates four sentiment codes with modifier recognition. Everything looked promising when we started testing.
Will your thoughts stay at the center? Absolutely, but you'll work for it. All of your AI output gets saved as memos and annotations you can review, accept, or reject, which gives you more control over results. Whatever we gained in extra control was hedged by managing all those outputs. We found ourselves spending a lot of time organizing the AI's suggestions and forgetting where they lived.
Will it save you time? Eventually, yes. Initially, not at all. You need to code a substantial portion of your data before the pattern-based AI picks up on your coding approach, though the other auto-coding methods work straight away. The real issue is the learning curve with NVivo isn't just steep, it’s more of a cliff.
How transparent is the process? The transparency is solid after you understand the layout. NVivo documents its AI reasoning through saved memos, but navigating to those explanations isn't intuitive as other tools on this list. Methodological flexibility is there, but buried under layers of interface confusion.
Here's what we liked: The multi-language processing actually understands technical terminology, which impressed us even if we don’t have much use for this functionality. The three different approaches to auto-coding give you options depending on your methodology, and the sentiment analysis goes beyond simple positive/negative to include modifiers and neutral ranges.
What to keep in mind: NVivo's AI is sophisticated and powerful, but the platform has a laundry list of customer support issues. Getting help when AI features don't work could be an uphill battle. Other users mention the steep learning curve even for basic features was an unexpected roadblock. Learn more about what users are saying about the NVivo experience.
ATLAS.ti: Beta integration with pattern recognition
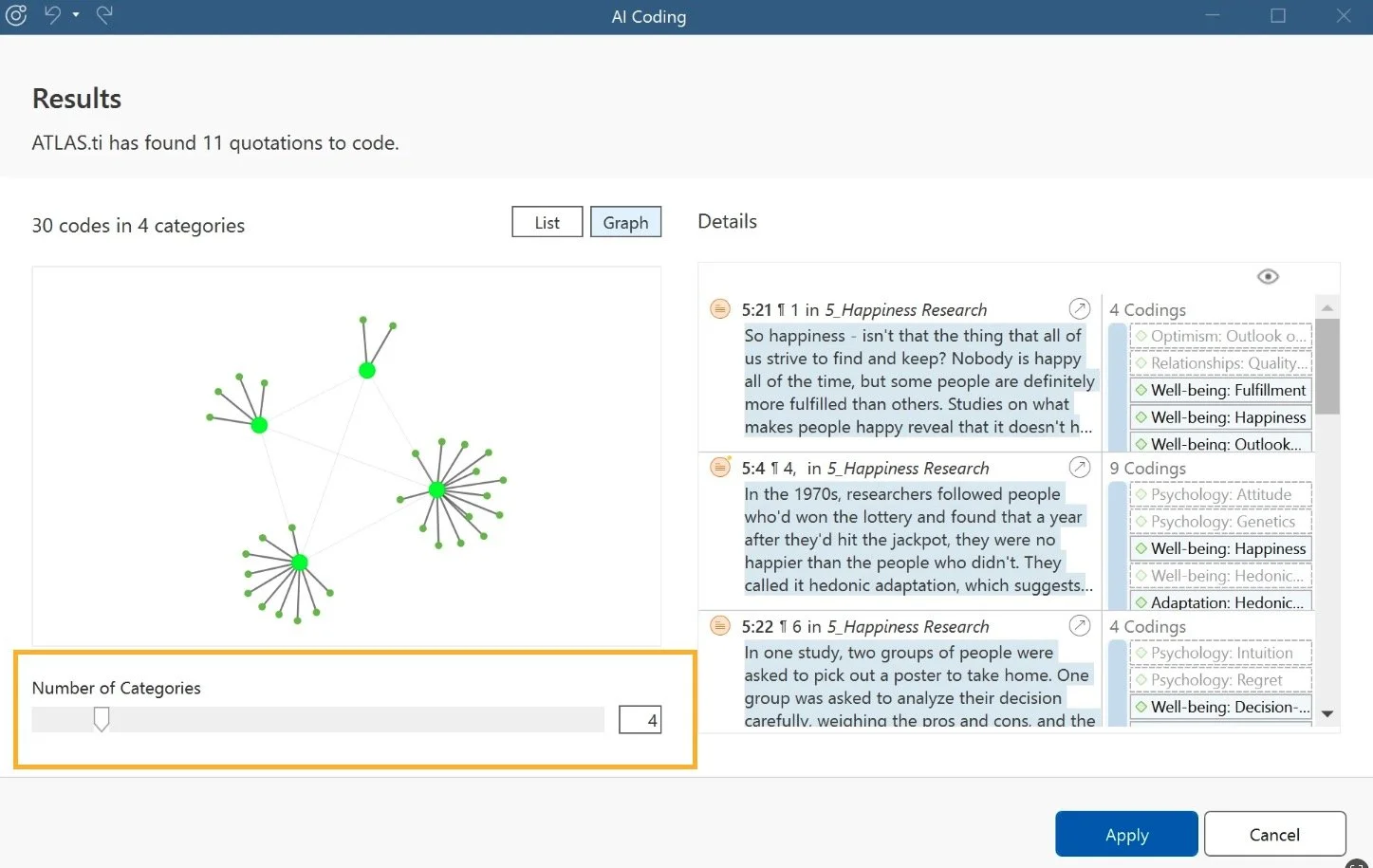
ATLAS.ti calls their beta AI Coding feature "the most powerful automated inductive coding tool" in QDA software. They might be right. The AI can generate an initial code structure automatically, organize codes into hierarchies, and even analyze multiple documents simultaneously. It's genuinely impressive AI integration, powered by OpenAI, wrapped in an interface that assumes you know what you're doing.
Beyond the headline AI features, the platform offers conversational AI that can query across documents, sentiment analysis, and automated pattern recognition. Unlike some competitors, ATLAS.ti's AI doesn't just apply existing codes – it could discover new patterns and suggest entirely new coding frameworks.
Will your thoughts stay at the center? Yes, with patience and practice. ATLAS.ti positions the AI as "your personal research assistant," but this assistant needs supervision. Every suggestion requires validation, and the system automatically organizes codes into hierarchies and subcategories. While validation makes sense, the sheer volume of AI-generated suggestions makes reviewing them a time-consuming task in itself. The control is there, but so is the cognitive overhead.
Will it save you time? Mixed results that depend heavily on your experience level. The AI can handle grunt work like applying established codes and spotting initial patterns, but learning to prompt it effectively takes time. We found ourselves frustrated with outputs that missed context we thought was obvious. When it works, you do see time savings, but getting there requires patience.
How transparent is the process? Reasonably good, but not intuitive. The AI explains its reasoning, but accessing those explanations requires navigating through multiple interface panels. ATLAS.ti provides "100% transparency," but you have to know where to look for it – and that takes time to learn.
Here's what we liked: The AI's automatic code hierarchies jump-started theme development. When we fed it interview data about remote work, it automatically organized codes like "isolation challenges" under broader categories like "social impacts." These structures gave us a solid foundation to refine rather than starting from scratch. The conversational AI feature goes beyond what most other tools offer by analyzing multiple documents simultaneously and pointing out evidence for your queries.
What to keep in mind: The sizable learning curve compounds when you add AI on top. ATLAS.ti assumes you know what you're doing, and the conversational AI requires careful prompting to produce useful outputs.
MAXQDA: AI with institutional privacy controls
MAXQDA's AI Assist add-on brings comprehensive AI functionality, but you'll pay twice – once for the base software, then again for AI features. If your budget can handle essentially doubling software costs, you get solid AI capabilities with MAXQDA's typically thorough approach to feature implementation.
AI Assist works similarly to NVivo’s AI options. You can ask it to summarize documents, get coding suggestions, analyze themes, and chat with your data. But different from Nvivo, this AI integration feels more like a part of MAXQDA rather than something they stuck on afterward, which helps when everything did run smoothly for us.
Will your thoughts stay at the center? Generally yes. MAXQDA's approach emphasizes "user autonomy" – you decide when and how to engage AI assistance. The system provides suggestions you can accept, modify, or reject, maintaining your control over analytical decisions, similar to Google Docs.
Will it save you time? Depends on your tolerance for MAXQDA's interface complexity and your budget for the AI add-on. The AI features work well once you understand where everything lives, but MAXQDA’s interface is not intuitive. We spent almost as much time figuring out how to access AI features as we did using them.
How transparent is the process? Good transparency aside from the complexity of the platform itself. The AI explains its reasoning, saves chat histories, and documents decision-making processes clearly. However, accessing this information requires navigating MAXQDA's complex interface.
Here's what we liked: The integration across MAXQDA's workflow feels natural rather than tacked-on. When it works smoothly, the AI genuinely feels helpful. Their approach to implementing AI emphasizes researcher control over automation, which we appreciated.
What to keep in mind: Aside from the underlying complexity of the software itself, recent reviews mention "frequent and unexpected crashes and data loss", which can lead to issues when you're relying on AI to speed up analysis. Users note that "the user interface of this software leaves a lot to desire" even before adding AI. 🌎
Delve: Focused AI designed for peer collaboration
Delve's AI Assistant focuses on being genuinely helpful with the specific tasks that slow you down without getting in the way. The AI works like it was built to work within your existing workflow. You can have natural conversations with your data (on your entire corpus or selected codes or transcripts) and ask it to format responses as tables, bullet points, or with snippet citations to get exactly what you need.
The conversational nature functions just like a virtual peer debriefer for discussing your findings, because you can ask it questions about your data and have back-and-forth discussions. If you want to ask your dissertation chair a question but they're unavailable or out of reach, you always have this second option as a backup to bounce ideas.
And after you create the codebook (you still control that) you can have AI apply your codebook deductively like it's a research assistant. It can also review code clarity and suggest improvements, which amplifies your analytical thinking. Unlike platforms where AI feels bolted-on, this integrates naturally with how most people already code.
Will your thoughts stay at the center? Yes, by design. Delve's AI doesn't try to "do the analysis for you." It supports your thinking process, applies a codebook, and helps sanity check results. You can apply and easily remove AI-applied codes, see clear reasoning for suggestions in AI memos, and maintain full control over your work. The AI acts like a helpful second opinion, not a replacement for your judgment.
Will it save you time? Yes, without the learning curve that other platforms impose. The AI assistance feels immediate and intuitive. You don't spend time learning to prompt effectively or managing complex AI outputs. It helps where you need it and stays quiet otherwise. The AI chat feature is particularly helpful when you want to ask your dissertation chair a question but they're unavailable.
How transparent is the process? Very clear. Delve shows why the AI suggested specific codes in the AI memos and maintains a chat history so you can track your analytical thinking. The reasoning is accessible and understandable. Like other platforms using OpenAI, your data on Delve’s “privacy by design” follows the OpenAI Enterprise Privacy Policy, so you own your data and the ability to delete it at any time.
Here's what we liked: The focus on practical help rather than comprehensive automation. The AI can summarize codes, help with initial coding, and make it easier to build a codebook. And the AI tools work hand-in-hand with Delve's intercoder reliability tools to track and improve how consistently you all code the data.
What to keep in mind: The trade-off is scope. You won't get sentiment analysis, automated theme discovery, or complex pattern recognition like the enterprise tools offer. What you get instead is AI that works immediately and doesn't get in your way. Learn more about using AI in qualitative research to understand how Delve's focused approach fits different methodologies.
Learn more about Delve's complete AI approach or dive into the 30-minute webinar below.
No AI at all: Quirkos, Taguette, and Dedoose
Some researchers prefer complete control over analytical decisions, and several platforms cater to this preference. The motivations vary – methodological concerns, privacy requirements, or simple preference for manual processes.
Quirkos offers zero AI by deliberate choice. The founder has written extensively about eight main concerns with AI in qualitative analysis: accuracy issues, embedded bias, lack of qualitative training data, ethical transparency problems, inability to understand lived experience, speed versus quality trade-offs, security risks, and academic integrity questions. The platform only offers automated transcription using OpenAI's Whisper model, available as a $12/month add-on, but this converts audio to text without touching your analysis.
What's interesting is the founder's opposition to AI in qualitative analysis. He writes about eight main concerns: accuracy issues, embedded bias, lack of qualitative training data, ethical transparency problems, inability to understand lived experience, speed versus quality trade-offs, security risks, and academic integrity questions. These concerns seem to touch every industry at the moment.
Taguette has zero AI capabilities whatsoever. This free, open-source tool focuses on basic highlighting and tagging with real-time collaboration. No automated suggestions, no pattern recognition, no AI assistance of any kind. If you're looking for complete control over every analytical decision, this absence actually works as a feature.
Dedoose offers only keyword-based auto-coding that searches for terms and surrounding text. Their "auto-excerpting" features rely on keyword-based rather than AI-powered interpretation. It's efficiency automation, not artificial intelligence.
The case for staying manual: All three platforms represent purely human-driven analysis. If AI assistance conflicts with your methodology, raises privacy concerns, or simply doesn't appeal to you, these tools maintain traditional qualitative analysis workflows without compromise.
Choosing AI that fits your research
AI tools for qualitative data analysis come in all shapes and sizes. The question isn't which has the most AI features, but which approach matches how you actually work.
➲ Choose sophisticated AI (NVivo, ATLAS.ti) when you want to:
Analyze large datasets requiring systematic pattern recognition
Save significant time on initial coding phases
Work with enterprise-grade tools and have proper security requirements
Invest time learning complex AI workflows
Handle technical troubleshooting when beta features break
➲ Choose focused AI assistance (Delve) when you want to:
Handle tedious coding tasks while keeping interpretation human-driven
Get virtual peer debriefing when working solo
See clear explanations for every AI decision
Learn quickly without complex feature overload
Collaborate on analysis without AI getting in the way
Maintain traditional analytical rigor with efficiency gains
➲ Choose privacy-focused comprehensive AI (MAXQDA) when you want to:
Support multilingual teams across international projects
Meet strict GDPR compliance with EU data storage
Access comprehensive AI with institutional controls
Work with menu-rich interfaces and extensive customization
➲ Choose no AI (Quirkos, Taguette, Dedoose) when you want to:
Keep complete human control over all analytical decisions
Work with sensitive data where AI usage violates protocols
Learn qualitative fundamentals through manual processes
Use theoretical frameworks that conflict with automated pattern recognition
The most practical qualitative research AI tools in our testing were those that let you easily reverse AI decisions. Being able to remove AI-applied codes, see reasoning for suggestions, and maintain full control makes the difference between helpful AI and frustrating automation.
🧭 Research priority matrix
| Your priority | Best AI option |
|---|---|
| Solo researcher or small team needing a research “assistant” | ✅ Delve (focused AI support, intuitive, peer-style debriefing) |
| Handling large datasets quickly | 🟡 NVivo or ATLAS.ti (deep automation, steeper learning curve) |
| Privacy and multilingual requirements | 🟡 MAXQDA (GDPR compliant, 11 languages, menu-rich) |
| Avoiding AI entirely, teaching fundamentals | ❌ Quirkos / Taguette (manual-first, minimal AI by design) |
| Mixed-methods, quantitative integration | ❌ Dedoose (keyword auto-coding, not true AI) |
The best AI for qualitative data analysis
Delve's AI Assistant makes you more efficient without replacing the analytical thinking that makes qualitative research so valuable in the first place. Tools that promise to "do the analysis for you" are likely going to miss the nuanced understanding that comes from deep engagement with your data. You want a trusted set of eyes and not a clunky distraction that gets in the way.
Delve's AI Assistant acts as a virtual peer debriefer to review and discuss your findings, and a virtual research assistant to help you deductively code your qualitative data. While you (a human) still need to design your study, understand the context, and construct meaning from your codes, Delve gives you a second opinion on your codes, and takes on grunt work to free up time for bigger-picture thinking.
If you’re looking for AI that lends a hand without getting in the way, start your free 14-day trial of Delve.
🤖 Trusted by researchers using AI to enhance their analysis
From undergraduate honors projects to doctoral research, students and researchers are discovering how Delve's AI features speed up coding while keeping human insight at the center. Users consistently highlight how AI assistance saves time and helps uncover insights they might have missed.
- "The AI tool helped add to my conclusions about the data... I appreciated the AI help feature as well." Read more
- "The AI coding was also helpful as I code in addition to what was done by the AI." Read more
- "The new AI feature is helpful with coding and exploring codes I may have missed initially." Read more
- "I loved that I could ask the AI questions about the data that I was curious about." Read more
- "I like the option as coding using AI which works really very and reducing half of your time on coding every transcript." Read more
Real researchers are already using AI to do better analysis – faster. Hear from more users.
Start Free 14-Day TrialNo credit card required. Cancel anytime.
Want to explore more QDA software comparisons?
Software Comparisons:
Methodology Guides:
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in QDA Software
Can AI actually understand qualitative data the way humans do? Not really. But AI is top-notch at pattern recognition and text processing. Just remember it lacks the contextual understanding, cultural awareness, and interpretive insight that human researchers bring to qualitative analysis. The best AI tools acknowledge this limitation and focus on supporting human interpretation rather than replacing it. This is especially important when conducting thematic analysis or grounded theory research, where human interpretation and theoretical sensitivity are core to your work.
How do I know if AI suggestions are accurate for my research? Always validate AI output against your raw data and research context. AI tools like Delve provide transparent reasoning for their suggestions and allow you to see chat history to track your analytical process. If an AI suggestion doesn't make sense for your specific research context, trust your judgment. Learn more about validating AI suggestions in our methodology guide.
What's the difference between AI coding and traditional auto-coding? Traditional auto-coding searches for specific keywords or phrases. AI coding uses language models to understand context and meaning, so it can identify concepts even when they're expressed in different words. However, AI coding still requires human validation to ensure accuracy and relevance. For detailed guidance on different coding approaches, see our Essential Guide to Coding Qualitative Data.
Can I use AI for sensitive research data? This depends on your institutional requirements and the AI tool's privacy policies. Platforms like MAXQDA offer GDPR-compliant AI with EU data storage, while others like NVivo provide zero-retention policies. Delve allows you to opt out of AI features entirely if your research protocols prohibit AI usage. Always check your institution's data governance requirements before using AI with sensitive research data.
How much time does AI actually save in qualitative analysis? The time savings depend on your project and how you use AI. Tools like ATLAS.ti claim up to 90% time reduction in initial coding, but this assumes you still need to review and validate everything. AI that tries to automate too much can actually waste time if you spend hours editing and cleaning up results that missed your research context.
Tools that overpromise immediate results often create more work downstream. More focused tools like Delve save time on specific tedious tasks(applying established codes, brainstorming subcodes) while keeping you at the center. This targeted approach tends to save more time overall because you're getting help with grunt work without constantly second-guessing the AI's interpretations.
What should I do if AI suggests codes I hadn't considered? This is one of AI's genuine benefits – spotting patterns you might miss. But evaluate any new suggestions carefully. Ask yourself: Does this make sense in my research context? Does it align with my theoretical framework? Can I find supporting evidence in my raw data? Use AI suggestions as starting points for deeper investigation, not final answers. This iterative process is particularly valuable in inductive coding approaches.
Can AI help with intercoder reliability? Somewhat. AI can help standardize how codes are applied by providing consistent reasoning, but human coders still need to establish the initial agreement on code definitions and boundaries. Delve's AI features can help team members apply codes more consistently, but they don't replace the need for human discussion and agreement in collaborative qualitative analysis.
Should I learn qualitative analysis manually before using AI tools? Yes. Understanding fundamental qualitative research principles helps you use AI more effectively and critically evaluate its suggestions. AI tools work best when you already understand the underlying process. They're meant to enhance skills, not replace the need to learn them. Start with our free qualitative coding course to build foundational skills.